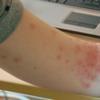
What Are the Signs and Symptoms of Hives?
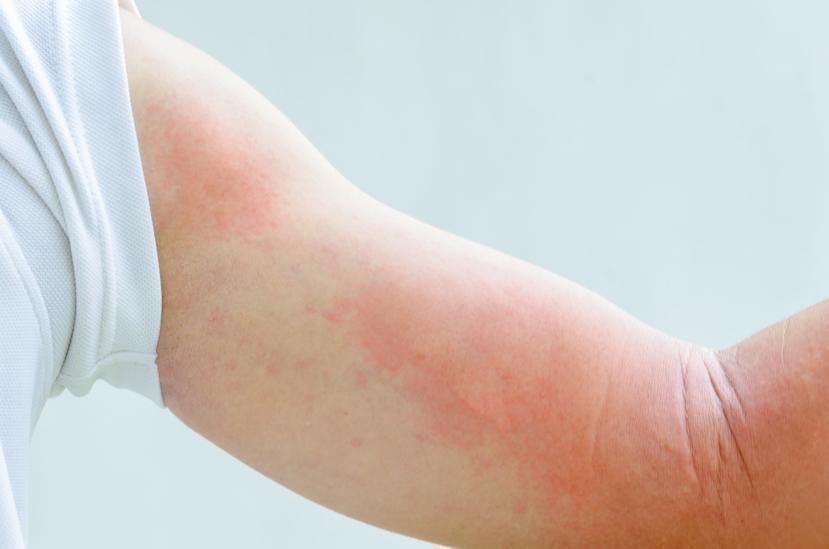
Swellings, referred to as weals, manifest on the skin as rashes. They are normally pink or red in color, possess an oval or circular shape, and may be surrounded by a reddish flare. Hives can be detrimental and awfully itchy.
The weals normally appear in batches, and frequently occur on the face, fingers, toes, arms, legs, or hands. A welt can vanish after some few hours but will be replaced by emergent ones. They may attack a specific part or several parts of the body.
For most acute cases, signs or symptoms last for 8 to 12 hours and hardly go beyond 24 hours. However, for some people, the problems might persist for a few days or months.
Acute Urticaria
Hives or urticaria is a skin condition characterized by a sudden development of a rash. The rash in urticaria appears as smooth elevated weals that are reddish in color. Most cases of hives are short term. This skin condition is usually accompanied by severe itchiness that may persist for some hours, but then resolves on its own afterwards. Although rare, some individuals may experience utricaria for several days or weeks. If the rash continues for more than six weeks, it is considered to be a chronic case of urticaria.
Risks and Complications
Angioedema has similar manifestations with hives with regards to producing reddish itchy weals on the skin. Their only difference is that angioedema affects your deeper skin layers, more particularly around your lips and eyes. Angioedema can become life-threatening if the affected parts of your body are your tongue and throat. The swelling of these body parts can cause a blockage in the airway.
Anaphylaxis
Anaphylaxis is a hypersensitivity allergic reaction, which is also referred to as anaphylactic shock. People suffering from this kind of immune reaction experience severe breathing complications and can even become unconscious, and lose their lives if they do not receive quick treatment. If you are suffering from hives, it is imperative to be more alert of any further symptoms that could designate an anaphylaxis reaction.
People who experience the following signs and symptoms should seek medical emergency services:
- Rapid heartbeat
- Nausea and vomiting
- Cold & clammy skin
- Faintness
- Difficulty in breathing caused by the swelling of the mouth lining, throat, lips, and tongue
- Unexpected intense feeling
- Extreme anxiety
Chronic (long-term) Hives
Chronic is medically defined as recurrent and long-lasting, which is usually characterized by extended suffering. In rare cases of chronic urticaria, the condition lasts for more than a month. Studies show that one in a thousand people experience chronic urticaria at some point in their lives. Women tend to be more affected by this skin condition than men. Moreover, there are other people who suffer from a recurring and irritating hives for several months up to years.
Signs and Symptoms
- Severe itching
- Clusters of red welts on the legs, trunk, face, and arms.
- Irregular swellings that cause extreme pain or burning, especially in the throat, cheeks, feet, genitals, eyes, hands, cheeks, and lips.
- Frequently recurring symptoms that could last for several months or years.
- Welts that occur in different sizes. They appear and vanish continually as the reaction advances.
- Symptoms that are triggered by stress, heat, and exercises.
What Causes Hives?
In usual cases, it is unknown as to what causes or triggers this type of skin condition. However, it is believed that the release of histamine, a chemical compound that is a part of our immune system, causes our skin’s blood vessels to dilate forming an inflammation that leads to the development of weals. Other possible culprits of hives include:
- Autoimmune disorders – if a person has an autoimmune disease, it means that his or her body produces antibodies that attack his or her own healthy cells. When urticaria happens to a person with an existing autoimmune disease, the antibodies produced by the body attach themselves to the skin’s cells, prompting the cells to release chemicals including histamine. There is still no concrete explanation as to why this certain body mechanism happens.
- Allergies – include reactions to specific types of food and medication. A parasitic infection may also be a cause of allergy but only in rare cases. Tests are available if a person’s condition is suggestive of an allergy.
- Helicobacter pylori infection - H. pylori is a bacteria that causes intestinal ulcers or bleeding in the stomach. When individuals suffering from an H. pylori infection are healed, their urticaria will also fade and resolve on its own.
- Inducible urticaria – its largest subgroup, physical urticaria, is a type of urticaria that is triggered by physical stimuli such as scratching, rubbing, applying pressure, extreme temperature, and direct sun exposure. There are different forms of inducible urticaria, and they are:
- Urticaria factitia – more commonly called as dermatographia or dermatographism. Individuals suffering from this kind of skin condition experience rashes after their skin has been rubbed or scratched. For this reason, a person can write on his or her skin by using his/her finger with applied pressure. After writing, the rashes emerge following the strokes that were made.
- Cholinergic urticaria – is a type of physical urticaria wherein the physical stimulus is heat. However, the main cause for developing urticaria is not heat, but by sweating. That is why the rashes for this type of itchy skin is commonly referred to as “heat bumps.”
- Cold hives – happens when the affected person develops itchy and reddish rashes due to an exposure to cold temperature, such as cold water, rain, or a cool breeze of wind. Young people are often affected by this type of urticaria.
- Delayed pressure urticaria – may occur four to six hours after an applied pressure on the skin. Usually, the symptoms of urticaria are seen after wearing close-fitting garments or doing any activity that includes application of pressure to the skin for a longer time like hammering.
When to Consult a Doctor
Be sure to see a medical professional if you have:
- Hives that consistently appear for multiple days
- Extremely itchy hives
- Symptoms that do not positively react to treatment
Seek emergency medical care if you:
- Feel unusual swellings on your tongue or throat
- Feel dizzy
- Have serious breathing difficulties or extreme chest tightness
Many incidences of hives have proven to be idiopathic, implying that no real cause is existent. Others are caused by viral and fungal infections, while a few could be triggered by certain medications, usually taken several weeks before the symptoms appear. When particular medications are implicated as the major cause of hives, the drug should be stopped immediately because testing is hardly available to substantiate the cause. Most often, drug-induced hives disappear within few days. If you stop using the drug and your symptoms will not fade away, it indicates that your medication wasn’t responsible for the hives.
Emotional Impact
Living with chronic hives can really be frustrating. It can have a huge impact on someone’s mood and life quality. Living with a severely itchy skin can be terribly upsetting.
Research indicates that long-term hives are equally harmful as heart diseases. It is also confirmed that one in every seven patients with chronic hives experiences some form of psychological problems such as depression, stress, and anxiety.
Hives Triggers
Hives/urticaria can immensely be triggered by:
- insect bites or stings
- certain medications like NSAIDs and ACE inhibitors
- sunlight
- certain foods
- extreme temperatures
- contact with chemicals, nettles, and latex