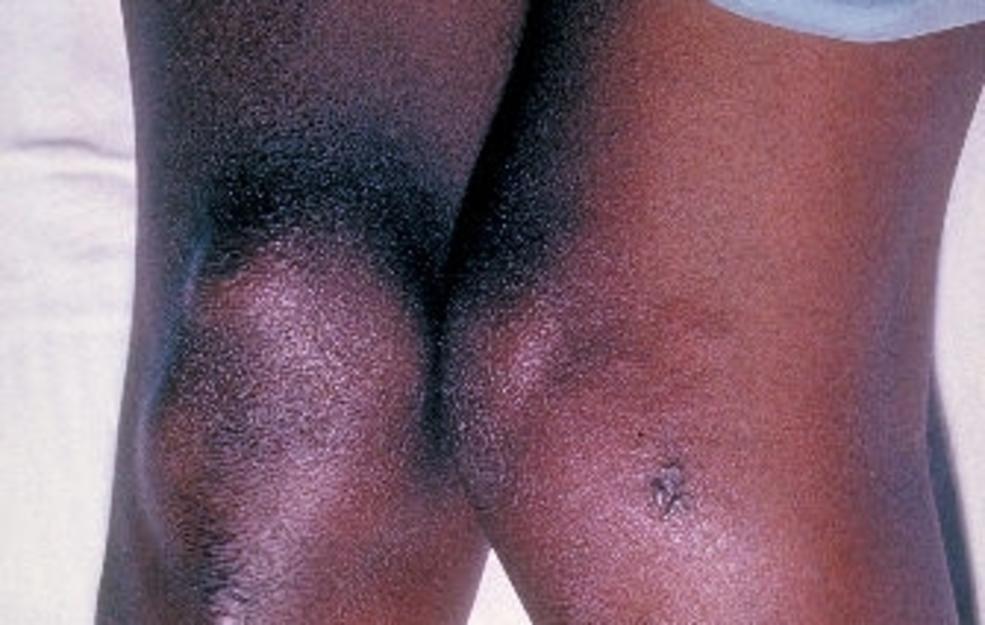
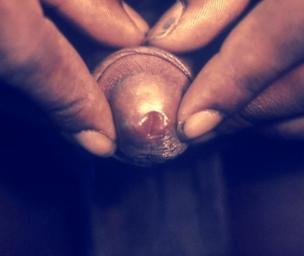
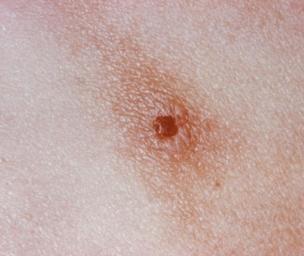
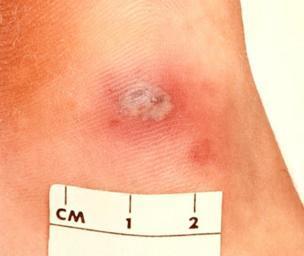
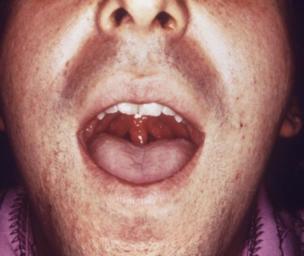
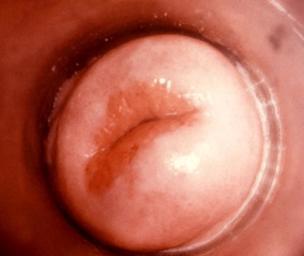
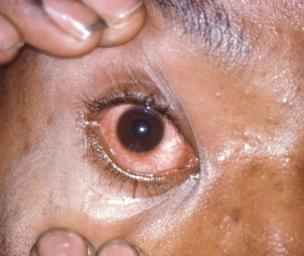
What Does Gonorrhea Look Like?
Gonorrhea is a sexually transmitted infection, which arises due to bacteria. It may cause infertility if not treated in time. Gonorrhea can cause several serious complications as well if not left untreated. Gonorrhea can be cured with timely treatment and medications. It can be spread by having vaginal, oral, or anal sex with a person who is infected with gonorrhea.
It is triggered by an infection from the bacterium Neisseria gonorrhoeae, which has a tendency to infect warm, damp areas of the body, including the eyes, throat, anus, vagina, urethra, and reproductive tract of females.
Gonorrhea passes from one person to another via unprotected anal, oral, or vaginal sex. Individuals with several sexual partners, or people who don’t use a condom are at the highest risk of getting infected. The best safeties against infection are self-discipline, fidelity, and proper condom use.
What Does Gonorrhea Look Like in Women?
A gonorrhea infection in women may induce vaginal bumps or swelling that causes discomfort while urinating or having sex. It can cause blisters in the mouth or anus, too.
What Does Gonorrhea Look Like in Men?
In men, the infection may look like a swollen penis and testicles, which have rashes or spots that make it uncomfortable to urinate or have sexual intercourse. The penis may also discharge a pus-like fluid, too.
What Are the Symptoms of Gonorrhea?
Symptoms generally appear within two to fourteen days after getting infected, however, some infected persons never develop visible signs. An individual with gonorrhea who doesn’t have any symptoms is still infectious, and such people are more likely to spread the disease to other partners.
Symptoms in Women
Many women do not develop any obvious signs of gonorrhea. When they do develop symptoms, they tend to be minor or resemble other infections, making it more difficult to recognize. Gonorrhea infections can look a lot like common bacterial infections or vaginal yeast infections.
Symptoms include:
- Vaginal discharge
- Pain while urinating
- Frequent need to urinate
- Heavier menstrual periods
- Sore throat
- Discomfort during sexual intercourse
- Severe pain in the lower abdomen
- Fever
Symptoms in Men
Men might not develop perceptible symptoms for many weeks, and some may never develop any.
Usually, the infection begins to show signs a week after its transmission. A common initial symptom in men is a burning or aching feeling while urinating. As it develops, other signs may include:
- Frequent urination
- A pus-like discharge from the penis
- Inflammation or soreness at the opening of the penis
- Inflammation or discomfort in the testicles
- Persistent sore throat
The infection will stay in the body for a few weeks after the signs have been treated. In rare cases, gonorrhea can continue to cause harm to the body, especially the testicles and urethra. Pain may also extend to the rectum.
What Are the Causes of Gonorrhea?
Gonorrhea is a contagious disease caused by the bacterium Neisseria gonorrhoeae. It affects the reproductive tract and may also affect the lubricant skins of the throat, eyes, mouth, and rectum.
The infection is spread through sexual interaction with an infected person via the vagina, anus, penis, or mouth. Men do not have to ejaculate to convey or obtain gonorrhea.
Gonorrhea may also be spread from an infected mother to her child during delivery.
Who Is at Risk for Gonorrhea?
Anyone who has sexual relations with a disease-ridden person is at risk. The threat increases when they do not use condoms or when they have various sexual partners. Gonorrhea can be spread through anal, genital, or oral sex. In the United States, the highest rates of gonorrhea contamination occur amid teenagers and adults in their twenties. People who have chlamydial infections or other sexually transmitted infections are more prone to having gonorrhea as well. All sexually active young men and women should be tested frequently for both chlamydia and gonorrhea.
Is Gonorrhea Contagious?
Gonorrhea is a contagious disease. When people do not use condoms or other protective methods while having sex, or they have several sexual partners, their risk of obtaining the disease increases. The infected individual can spread the disease to many others if not treated properly.
Gonorrhea-causing bacteria are diffused through body fluids, such as discharge from the vagina or semen, which are carried from one person to another during anal, oral, or vaginal intercourse. Infected mothers can also pass it to their babies during childbirth.
People can expose themselves if they touch an affected area and then touch their eyes. It can also be passed through kissing if one partner has a bleeding wound on the lip, but this way of getting infected is uncommon. Using towels and sitting on toilet seats that have come in contact with an infected person do not spread the infection.
Diagnosis of Gonorrhea
A diagnosis of gonorrhea involves the doctor using a swab or pad to take a sample of fluid or liquid from the cervix in women or from the urethra in men. The sample will then be sent to a laboratory to be examined. You may also be asked to give an anal or throat culture to check if the infection is in either of these areas.
Treatment of Gonorrhea
Common treatment for gonorrhea is antibiotics like ceftriaxone and cefixime, given as an injection. You may be prescribed an antibiotic called azithromycin, which is taken in tablet form, at the same time to help treat a chlamydia infection, if any, as it is very common for people to get both infections at the same time.
It is recommended your partner be tested if you are diagnosed with gonorrhea, as the chances of them getting infected are very high.
If a mother is infected with gonorrhea, she may pass it to the baby during delivery. These babies are given medication in their eyes immediately after birth to prevent infection. If an eye infection takes place during the delivery, babies can be treated with a course of antibiotic medicines.
There are currently no home remedies or over the counter drugs to treat this infection. Seeking medical help if the upmost priority of the individuals suffering from this disease.
Complications
Gonorrhea if diagnosed should be promptly treated. However, if the individual is not treated on a timely manner then it can lead to certain complications or risk. There can be serious and permanent health problems in both men and women. In case of women, an untreated gonorrhea can lead to pelvic inflammatory disease, it can lead to blockage of fallopian tubes with the formation of scar tissues, pregnancy outside the womb which is also known as ectopic pregnancy and it can lead to serious complications to the individual, inability to get pregnant again and chronic abdominal pain.
In case of men an untreated case can lead to excessive pain in the tubes which are attached to the testicles. In certain rare cases it can prevent the individual from being able to father a child in future. Though very rare but in certain conditions gonorrhea can spread in other parts of the body such as blood or joints which can then get life threatening. It also leads to an increase in the risk of getting HIV which is another sexually transmitted disease.
Prevention
The only safest way to prevent this medical condition or for that matter any sexually transmitted disease is through staying away from sex. However, if there is a need to indulge in sex then do so by using condoms. It is very essential to be open with your sexual partners and also get regular testing for STD related diseases. Avoid any sexual contact with the partner is showing any symptoms pertaining to the infection.
Ask them to reach out to medical help to rule out the possibility of an infection and avoid passing the same to others. An individual is at higher risk of getting this medical condition or any other STD if they had it earlier or if you have multiple sexual partners.