Chickenpox: Important Facts, Causes and Home Remedies
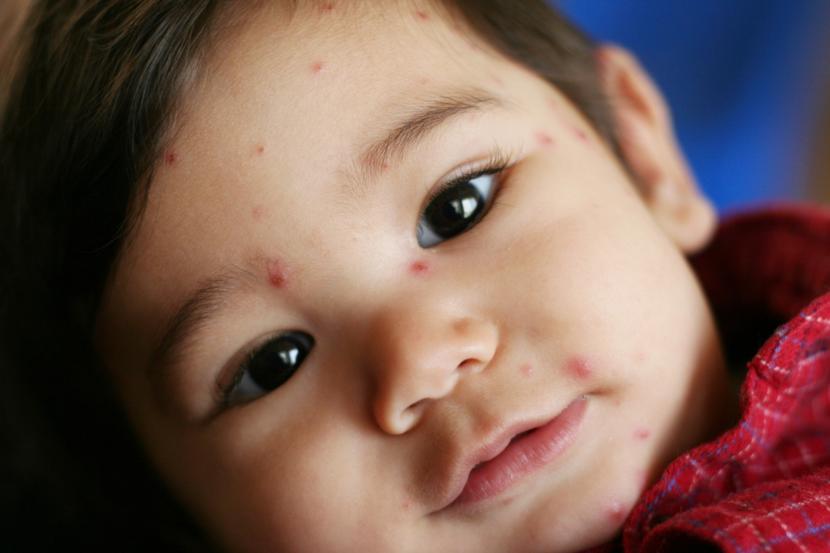
Chickenpox, also known as varicella, is a very common condition that occurs in most individuals either during their childhood or in adulthood. It is not a very serious condition, however depending upon the age and intensity with which it occurs, it could result in a lot of discomfort for the patient.
Important Facts About Chickenpox
Although there are vaccines that are available for chickenpox, it does not guarantee that it will not occur for those who have been vaccinated. If as a parent, you have your set of apprehensions and fears about chickenpox, then here is what you should know:
- Chickenpox often occurs as an itchy, red rash: The first signs of chickenpox start appearing around the face as itchy red coloured rashes that are filled with fluid as they progress. The signs and rashes start appearing on the face and slowly spread to the remaining body. The blisters could also appear in the mouth, eyes, and the lower body. The chickenpox blisters also progress in stages moving from red bumps to pus filled blisters to dried scabs. There are other signs also that could accompany the chickenpox disease like high or low grade temperature, body pain and tiredness. People normally feel sick and experience symptoms for anywhere from one week to ten days.
- Chickenpox could spread rather fast: Chickenpox is a disease that is known to be highly contagious as it spreads through air as one coughs or sneezes. The disease is so contagious that the rashes stay on till they become dried scabs. A person who is suffering from chickenpox is known to be contagious one or two days before the blisters become scabs. If you child is suffering from chickenpox, then it is best to keep them at home and not send them to school as the infection could easily spread to others.
- Usually the disease is mild, but could become serious in no time: It is the discomfort and irritation that accompanies chickenpox that is more bothersome than the actual disease. However, sometimes a patient could also experience various symptoms like dehydration, pneumonia, respiratory troubles, bacterial infections and so on, which could cause secondary issues. People with compromised immunity levels like babies, older adults, pregnant women and people suffering from other health conditions are more likely to develop secondary complications due to the chickenpox virus.
- Chickenpox is no more a common disease: Prior to the chickenpox vaccine coming into place in 1990, this disease was one of the most common childhood diseases. However, recently the instances of the disease has decreased significantly which encourages more and more people to take the vaccine as a part of the mandatory vaccines taken during the early years of life.
- Chickenpox disease is manageable at home itself: In most cases, your child may not be asked to be brought to the clinic and be advised to rest at home, to lessen the risk of spreading the infection. Medications may be prescribed to deal with symptoms like fever and body pains.
What Causes Chickenpox?
Varicella is one of the most famous dangerous diseases that is easily spread from one individual to another. This disease is caused by the varicella zoster virus (VZV) which affects the nerves and is known to be among the herpesviral diseases. When one is infected with the virus, it stays in the body for a long time and doesn’t show any symptoms. Once you are infected, the varicella virus finds its way into the system where it later leads to the formation of the herpes disease known as shingles.
Varicella stays in the body for two weeks after one comes into contact with the disease and sometimes the signs and symptoms may be experienced after about three weeks. In most cases, it takes one or two days before one's temperature starts to rise. A rash then appears on the skin, often indicating the infection of the disease.
Varicella for the unvaccinated is more pronounced than for the vaccinated people. The first sign normally observed is the rash that occurs on the skin at the onset of the virus. The rashes then travel to the macules and then to the papules and later develops in vesicles, forming pronounced lesions that finally burst. The rash is normally first observed at the head, on the backside of the body and then at the chest. These lesions, despite eventually appearing all over the body, are mostly concentrated on the back and chest.
For healthy children, the varicella disease does not have any severe effects. Their temperature may rise, they will suffer from itchy skin and generally feel weak for a few days, but they will recover. For unborn babies, older people, and those with poor immune systems, varicella can be fatal. Due to their increased susceptibility to disease, varicella may bring on other diseases. After one has suffered varicella, it is very unlikely they'll get it again. It can even protect against other diseases; this virus helps provide antibodies that protect the body against future disease.
For the vaccinated, sometimes ther person can get infected again with another type of the virus over a duration of forty-two days. This type of varicella virus is normally very mild. Normally, these people have high temperatures and few skin blisters that don’t develop any further. They suffer for a shorter duration compared to the unvaccinated. The rash is observed to be maculopapular instead of vesicular.
Since the signs of the second attack of the disease are not extreme, it is hard to test this disease with only a clinical check-up. A laboratory test is also needed to ascertain which disease this is. For those who have been given the varicella vaccine twice, no re-infection has ever occurred, except some extremely rare cases. Some issues arise with varicella-like pneumonia that occurs in adults and bacterial infections that occur on the skin and tissues of the child. Other complications from varicella are encephalitis, toxic shock syndrome, osteomyelitis, haemorrhages, cerebellar ataxia and necrotizing fasciitis.
How Long Does the Infection Last?
The chickenpox infection normally lasts from about a week to 10 days in case of children. However, in case of adults the virus strikes with a higher intensity taking from 10 to 21 days to recover completely. The intensity with which the disease strikes is directly proportional to the immunity levels of a person and hence people with compromised levels of immunity are likely to suffer more.
Managing Chickenpox at Home
Chickenpox as a disease is associated with a lot of discomfort that a person goes through in every phase of the disease. One of the biggest challenges is to manage the infection and prevent it from spreading to others. Here are a few things to be kept in mind if you are dealing with a chickenpox patient at home.
- Although the blisters caused due to chickenpox may be extremely itchy, it is best to avoid itching as scratching these blisters could cause scarring that is hard to go away. It is also important to keep the nails trimmed so as to prevent the blisters from breaking or bleeding due to scratching.
- Cool baths with some baking soda is the best remedy to get rid of the itching in a safe manner.
- Use calamine lotion to get rid of the burning sensation caused by the blisters. Calamine lotion is a safe remedy that provides a cooling effect and also brings about relief from the severe itching sensation.
- It is extremely important to keep drinking water, as chickenpox could all of a sudden push a patient into a dehydration zone which could be risky, especially in case of small children. Fluids like coconut water are very cooling for the body in case of diseases like chickenpox and also supply essential electrolytes to the body that is important in the recovery process.
- Chickenpox calls for a healthy diet management for the patient, as healthy foods promote a healthier functioning of the immune system. Say no to junk, oily and fried foods and stick to bland foods or fruits for better nutrition.
- Neem leaves are an age old remedy to treat chickenpox and manage the condition effectively. In traditional ayurveda, neem has been known for its antiviral properties and helps a great deal in combating the infection and purifying the atmosphere so that the virus is unable to spread. Neem leaves are spread around the bed of the infected person and a paste made out of neem leaves is applied on the dried scabs to prevent itching. Neem provides a cooling effect which also helps in getting rid of the burning sensation. Fanning with neem leaves and having a bath with neem leaves is also a common practice when it comes to managing chickenpox.













