Everything About Oral Thrush

What is oral thrush? How does oral thrush develop? What are the risk factors of developing oral thrush? What are the signs and symptoms of oral thrush? Is there treatment for oral thrush? And if it is there, what is it? These are just but some of the questions you may be asking yourself and are yet to receive answers. You need not to worry any more, as that is the goal of this article – to answer these questions.
Take some of your time to study this article to get knowledge of everything you need to know about oral thrush.
What is oral thrush?
Oral thrush is a fungal infection of the mouth. It is caused by a fungus known as Candida albicans, commonly known as yeast. Therefore oral thrush is also known as oral candidiasis.
Candidiasis infections not only occur in the mouth, but can also occur in other parts of the body such as vagina. They can also occur in the form of diaper rashes in infants.
Thrush can affect anyone but it most commonly tends to occur in babies, toddlers, elderly individuals and in those with a weakened immune system.
How does oral thrush develop?
Everyone has candida growing inside their body but not everyone develops thrush. Why is this? This is because in all healthy individuals, candida is kept in balance by the body’s immune system. It is when this balance is interrupted that one develops thrush due to the overgrowth of Candida.
This overgrowth may be triggered during:
- Illnesses that weaken your immune system
- Pregnancy
- Medications that suppress the immune system such as corticosteroids and anti-cancer drugs.
It is quite common to see most new-born babies and infants develop candidiasis. But unless it causes poor feeding or a loss of weight, it should not be a concern.
What are the risk factors for developing thrush?
Not all healthy individuals develop oral thrush. You need to have certain risk factors in order to develop thrush. Those with a weakened immune system are more likely to develop oral thrush owing to the fact that the weak immune system is unable to maintain the balance of candida organisms.
The risk factors of thrush include the following:
- Illnesses such as poorly controlled diabetes mellitus, HIV/AIDS or cancer.
- Pregnancy
- Medications that suppress the immune system such as corticosteroids, chemotherapy, radiation or Oral contraceptive pills (OCPs).
- Smoking
- Stress
- Undergoing an oral transplant – These patients are usually given medications to suppress their immune system to avoid rejection of the organ.
Thrush is not contagious disease. That means it does not transmit from one person to another. However, it could be transmitted from a breast feeding baby to the mother’s breast through contact.
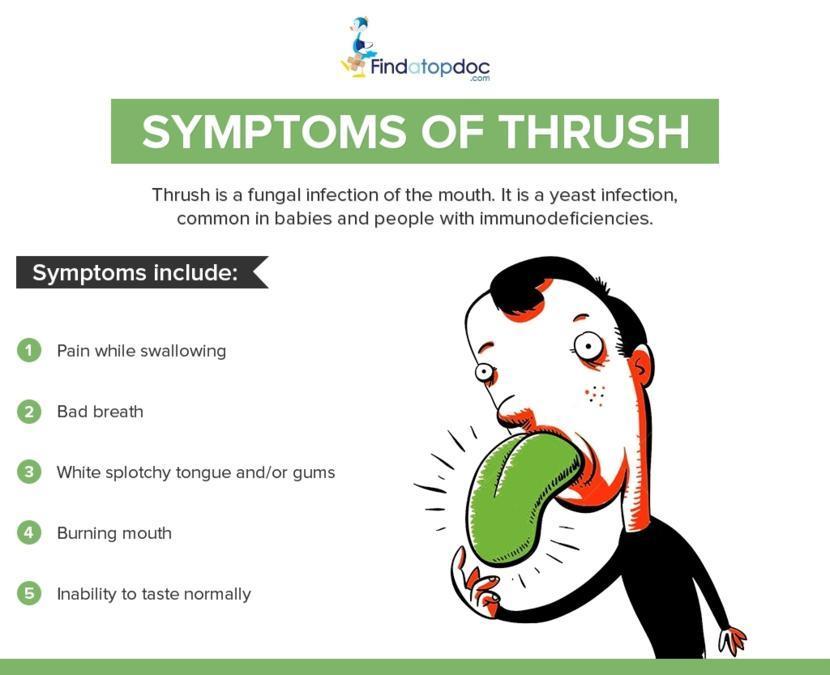
What are the signs and symptoms of thrush?
The symptoms of thrush appear all of a sudden and it can become a chronic, persisting infection that lasts for several years.
The most commonly seen sign in oral thrush is the development of a creamy, white lesion that is slightly raised in the mouth, tongue or the inner cheeks. This lesion could also develop over the roof of the mouth, gums, and tonsils and at the back of the throat.
The whitish lesion resembles a “cottage cheese” or “milk curd” appearance which is a characteristic feature in all forms of thrush. Oral thrush can be painful and may cause minor bleeding when scratched or while brushing teeth.
Other features of oral thrush include the following signs and symptoms:
- Dry mouth
- Bad breath
- An unpleasant bitter taste in the mouth.
Sometimes, in severe cases of oral thrush, the infection can spread to your oesophagus causing difficulty in swallowing referred to as dysphagia. It can also cause a feeling of food stuck at the back of your throat and fever.
In people with a weaker immune system can get much worse. This infection could spread throughout your body including your lungs, liver and skin in these people.
How is thrush diagnosed?
Your physician or dentist can easily diagnose oral thrush with just the examination of your mouth. The characteristic white plaques with a resemblance to milk curd or cottage cheese helps in the diagnosis of thrush. However, if ever a suspicion about the diagnosis arises, then your physician or dentist may take a small amount of the scraping from the whitish lesions and will have a look under the microscope. The characteristic fungi shape will help them to diagnose oral thrush in you.
If your candidiasis infection has spread to your oesophagus and below, then other methods will be needed to diagnose thrush. Such tests include:
- Throat culture – Using a sterile throat swab, your physician will take a throat swab and will send this to look at the microorganisms under a microscope.
- Upper gastrointestinal endoscopy – This procedure is usually done by a gastroenterologist and is helpful to look for candidiasis infections in your oesophagus or the stomach. During this procedure, they insert a small tube with a video attached to it, to examine your oesophagus and stomach. If any white patches are discovered, then they will take a small biopsy from them for microscopy to confirm the diagnosis.
- X-rays of your oesophagus
How is oral thrush treated?
Upon knowledge of suffering from this condition, do not rush to use over the counter drugs unless prescribed by the doctor. There are several causes and the results of the diagnosis done will lead in determining the necessary medication alongside something else. Read below for more information.
Healthy individuals can be easily treated with anti-fungal medications to treat oral thrush. On the other hand, treatment will be difficult in those with a weakened immune system. Anti-fungal medications come in several forms including tablets, lozenges or liquids and they are supposed to be taken for a period of 10 to 14 days.
The drug that will be prescribed to you will be decided by your physician depending on your age and the cause of infection.
Since oral thrush can be the result of several other medical conditions, your physician may ask you to run out further tests to exclude these possibilities. If such medical problem is detected, then treatment for it will be started.
Apart from the anti-fungal medication, other measures like controlling of your diabetes, and stopping smoking should also be carried out to gain complete cure. However, infants and toddlers do not require any treatment unless it has been persisting for several weeks, reduced feeding, the baby has lost weight or any combination of these symptoms. If such circumstances develop, take your child to a pediatrician as early as possible. They may start an anti-fungal such as Nystatin to cure the infection.