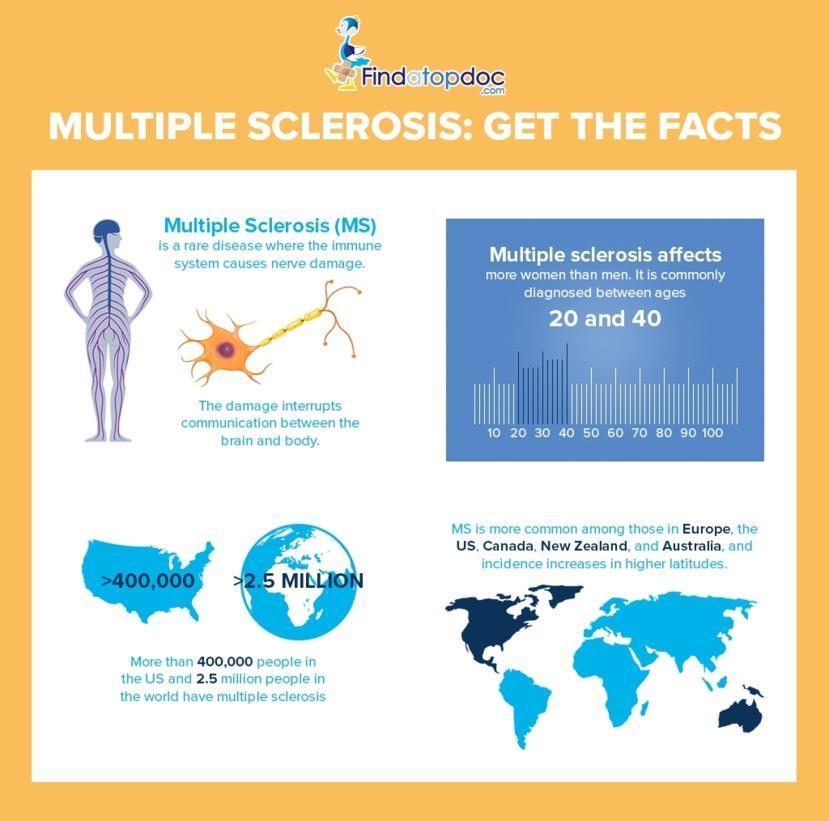
Everything You Need To Know About Multiple Sclerosis

Causes
MS is the result of an abnormal response of the body’s immune system. This response results in an attack on the central nervous system — the brain, spinal cord and optic nerve. Specifically the immune system attacks the protective coating around the nerve fibers — myelin — creating scar tissue on and around the nerves. This scar tissue interrupts the impulses that travel to and from the central nervous system, resulting in many debilitating symptoms.
Symptoms
MS is a disease that is unique to each individual, with symptoms varying from mild to severe. Primary symptoms are those that come directly from the damage to the myelin sheaths, such as the inability to release urine from the bladder. Secondary symptoms arise as a consequence of primary symptoms. For example, the inability to release urine from the bladder may cause a bladder or kidney infection.
Symptoms of Multiple Sclerosis
- Numbness, feeling of “pins and needles”
- Frequent urination
- Constipation
- Muscle weakness or spasms
- Balance problems
- Fatigue
- Dizziness and lightheadedness
- Low sex drive
- Speech problems
- Difficulty swallowing
- Slowed thinking
- Tremors
- Vision problems
Tertiary symptoms of multiple sclerosis are the psychological, social, and job-related difficulties that come with living with this chronic illness. For example, an individual that has muscle spasms or dizziness may no longer be able to drive and has to rely on public transportation or support of other people for visiting a doctor even.
Types of Multiple Sclerosis
According to the American Academy of Neurology, there are four distinct types of MS:
1. Relapse-Remitting (RRMS) - Unpredictable periods of worsening symptoms (relapse) followed by full remission of symptoms.
2. Primary-Progressive (PPMS) - Slow, worsening symptoms with no relapse or remission
3. Secondary-Progressive (SPMS) - Steady, worsening symptoms with no relapse
4. Primary-Remitting (PRMS) - Slow, worsening symptoms with occasional relapse
Treatment
Although there is no cure for MS, there are many therapies available to minimize the impact of the disease and treat the symptoms. Disease modifying therapies aim to reduce the occurrence of relapse and slow the progression of the disease. Symptomatic therapies do not impact the progression of the disease, but may lessen the severity of some symptoms.
Therapy Options for Multiple Sclerosis
- Physical therapy
- Speech therapy
- Occupational therapy
- Cognitive rehabilitation
- Balance therapy
- Exercise therapy
- Respiratory therapy
Medications can be used to modify disease progression, treat relapses, and manage symptoms of multiple sclerosis. Medications include Avonex, Capaxone, Aubagio and Lemtrada to alter the progression of the disease. These medications come in many forms, such as injectables and infusion therapies. A variety of medications are available to manage symptoms such as botox for bladder dysfunction, prozac for fatigue, and klonopin for muscle tremors.
It is important to note that mental health support is a necessary part of treating this chronic illness. Decreased function and reduced mobility can cause depression in individuals with multiple sclerosis. Psychiatric care, counseling, and support groups are important for maintaining emotional and psychological well-being.
Living with Multiple Sclerosis
Management of multiple sclerosis is an ongoing process that begins with the treatment of the very first symptoms. Comprehensive care including therapy, medication, and psychological treatment and complementary medicine are necessary for the management of this complex disease. With the right combination of treatments, many individuals with multiple sclerosis are able to manage symptoms, maintain function and generally live well.