Have You Heard About the Various Types of Depression?

Depression is a state of mind wherein people feel sad, anxious, and upset all the time. It is a mental condition that affects the way a person thinks, feels, and behaves. Depression happens when people's thoughts turn completely negative and they later become distant avoiding any form of social contact.
There are a number of myths associated with depression as a medical condition, and these myths can influence depressed people to avoid discussing their state of mind openly with others. People who are depressed often fear of being misjudged or ridiculed. For this reason, they are hesitant about seeking medical help. The social stigma that is associated with depression and medical ailments is also responsible for holding people back from reaching out to healthcare professionals to discuss their issues.
If you are suffering from depression symptoms or are concerned about a loved one who may be depressed, it is helpful to know the various types of depression and what category one falls under:
- Melancholia: Melancholia is a severe form of depression, which involves a number of physical symptoms that characterize depression. People who are affected by this kind of depression are likely to suffer from loss of interest and pleasure in everything including doing the activities that they really enjoy. Physically, there can be body signals that can indicate depression, and one of the major signals is having a sluggish body movement.
- Psychotic Depression: In some cases of depression, people may lose themselves to another state of mind that is not in consensus with reality. In other words, people with psychotic depression are in a psychosis state of mind. Sometimes, people who are troubled can lose touch with reality and experience psychosis. They are often observed to hallucinate, experiencing severe negative feelings like fearing evil spirits or having the feeling of being followed all the time. They keep away from social gatherings as they believe people around them are against them and have negative intents towards them.
- Bipolar Disorder: Bipolar disorder is a rather fluctuating mental disorder wherein people experience various bouts of depressions. This mental disorder is also known as "manic depression" since people who are bipolar experience periods of depression along with bouts of mania. In between these mood swings, they also experience normal moods. Unlike in depression, mania is a condition wherein a person suddenly exerts too much energy, talks too fast, and has fast racing thoughts as well as ending up feeling great. Bipolar disorder has a lot to do with genetics and heredity. Anxiety, stress, and disturbing clashes can be triggers of bipolar disorder in some people. Diagnosing this form of depression will depend on the observance of its symptoms. A number of cases do not get properly diagnosed as bipolar depression. For this reason, there might be people who cannot get the appropriate treatment required for their condition.
- Perinatal Depression: It is also known as "postpartum depression". This medical condition affects a number of new mothers after they have given birth to their baby. This form of depression is caused by the pregnancy hormones playing havoc with the body by converting happy motherhood feelings into baby blues. Some emotional factors along with changes in the body during pregnancy can cause anxiety and fear, which can eventually lead to depression. The symptoms that are associated with this type of depression include feeling irritated, stressed, anxious, having extreme mood swings, tiredness, and lack of sleep. Most of these symptoms are known to last for one to two weeks after delivery, depending on the treatment taken and the intensity of the depression.
- Catatonic Depression: This type of depression is rarely seen among people who are depressed. This condition affects the motion and speech of individuals. It also causes the affected people to stay speechless or motionless for a long period of time. Catatonic depression is associated with a brain malfunction, wherein the neurotransmitters that allow communication between brain cells are less frequently produced. This condition often comes along with other health issues that may be neurological or psychiatric in nature.
- Geriatric Depression: This type of depression is associated with the elderly people. In a geriatric depression, the common symptoms are mood swings as well as mental and emotional sadness. The symptoms of this form of depression include hopelessness, worthlessness, isolation, changes in food choices, suicidal tendencies, and constant body aches and pains. In some cases, the elderly tend to experience pains and aches that cannot be clinically explained. These aches and pains are largely attributed to this form of depression.
- Endogenous Depression: This condition a major depressive disorder that is also known as "clinical depression". It is a form of depression wherein the patient remains sad and upset for a long period of time. These feelings tend to negatively affect the individual's moods and behavior, which will eventually make it difficult for the person to effectively carry out day-to-day activities. A number of genetic, environmental, psychological, and biological factors can culminate into this form of depression. Losing a loved one, a failed relationship, or trauma such as having an abusive relationship or rape can cause stress leading to an endogenous depression. The symptoms of endogenous depression include aches and pains, lack of interest in any activities, loss of focus, inability to concentrate or think clearly, loss of appetite, and binge eating.
- Dysthymia Depression: The term "dysthymia" is a Greek word, which is defined as "a bad state of mind". This kind of depression is also known as "chronic depression." It is characterized by a serious mood disorder and is known to affect more women than men. In dysthymia, patients will experience bouts of normalcy followed by periods of depression.
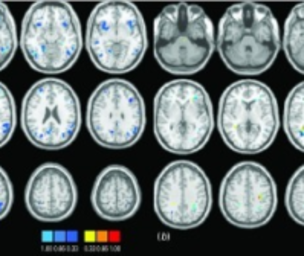
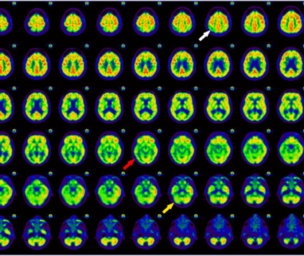
How does depression affect the brain?
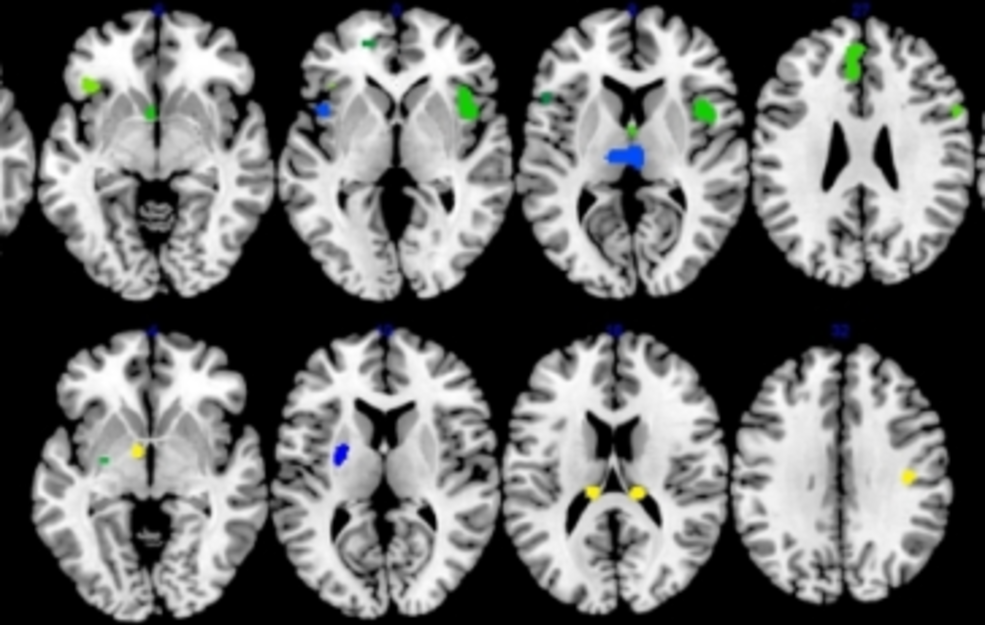
Depression is a mental condition that affects the way one thinks, feels, and behaves. It affects the brain negatively and causes one to react more negatively than one would under normal situations. To understand the impact of depression on the brain, let us first know its three parts, which are known to be involved when people are in a state of depression.
1. Hippocampus
The hippocampus is situated near the brain’s center. It is responsible for storing memories and regulating the production of the hormone called cortisol. At times of stress, when the body is experiencing anxiety and other forms of physical and mental pressures, this hormone is released. The same goes in the case of depression. The severity of depression arises when there is an excessive cortisol release at times of high levels of stress. This mechanism results in a chemical imbalance in the body. Long-term depression or stress can lead to a prolonged exposure to cortisol, which causes the cells in the hippocampus to shrink. This imbalance results in problems that are related to the thinking and recalling power of the brain.
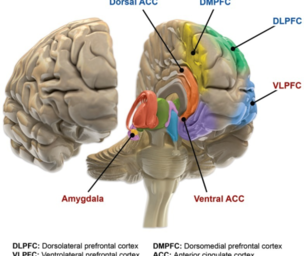
2. Prefrontal Cortex
Excess cortisol production is also felt on the prefrontal cortex, which is located in front of the brain. This part of the brain regulates emotions and processes them to form memories. High levels of cortisol also cause the prefrontal cortex to start shrinking, thereby making it difficult for a depressed individual to handle emotions.
3. Amygdala
The amygdala is the part of the brain that helps it understand and process emotional responses such as happiness, fear, and anxiety. When there is an excess production of cortisol, the amygdala becomes enlarged and hyperactive. This reaction can result in disturbed sleep patterns and hormonal imbalances in the body, thereby causing the symptoms of depression to worsen.