Trazodone: Withdrawal, Abuse, and Overdose

Trazodone Abuse
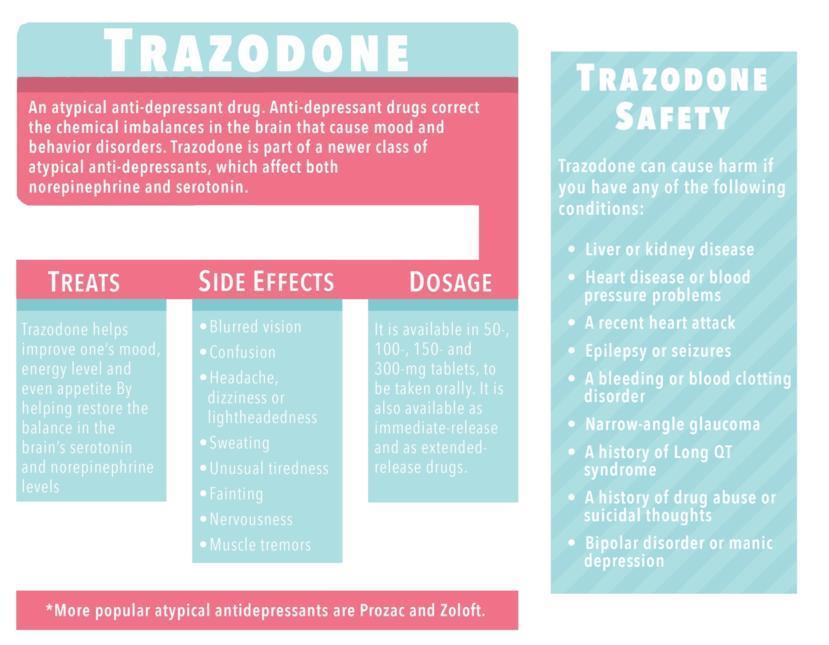
Trazodone is an antidepressant drug which is prescribed to treat and manage major depressive disorder. Depression is a mental disorder which causes extreme feelings of sadness and loss of interest in activities and life.
Trazodone must be taken with care because its effect on the chemicals in the brain can lead to abuse and in the long run, can become addictive. It works by blocking the activity of serotonin receptors in the brain as well as prevents serotonin from being reabsorbed by neurons. Thus, the serotonin level in the brain increases. Serotonin is a neurotransmitter which helps control different neurological effects, especially mood.
Trazodone can also be used to treat insomnia and anxiety. It is sold in under different brand names such as Desyrel and Oleptro.
The most common forms of antidepressants are tricyclic antidepressants, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), and serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs). Trazodone does not clearly fit in any of the categories mentioned as it is a unique form of antidepressant and is regarded as atypical. However, some experts say that it can be categorized as a serotonin reuptake inhibitor and serotonin antagonist.
Despite trazodone’s ability to help manage several types of mental disorders, trazodone has become significant in recent years because it has become more likely than ever to be abused. Trazodone abuse may start when the prescribed dosage is not working anymore because a drug tolerance has already developed. In this case, people will continue to increase their dosage and overuse trazodone. Over time, addiction is also developed. Another reason for trazodone’s addictive quality is that this drug works rapidly and can reach its maximum effectiveness within an hour after ingestion. Since it is fast acting, it seems to provide a quick fix to life’s problems. When trazodone is combined with other substances, such as alcohol, it has even more possibility of abuse.
Common Side Effects of Trazodone
- Drowsiness
- Constipation
- Blurred vision
- Sweating
- Dry mouth
- Muscle pain
- Sexual dysfunction
- Confusion
- Muscle pain
- Numbness or tingling
- Digestive problems
- Mild headache
More serious side effects of trazodone include:
- Restlessness
- Agitation
- Chest pain
- Extreme mood swings
- Sleep problems
- Dizziness
- Fainting
- Bruising
- Bleeding
- Shortness of breath
- Unconsciousness or coma
- Irregular or increased heartbeat
An individual can experience withdrawal symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, dizziness, irritability, seizure, trouble sleeping, headache, and psychosis when trazodone is stopped suddenly.
Although antidepressants can treat depression as well as insomnia, there is a high possibility that a person taking an antidepressant will be dependent on it to have a good sleep and to feel good. Even though trazodone is one of the antidepressants that are least likely to be abused, the probability is still there.
To shed some light on this matter, there are reports which found that there are people who snort trazodone to get high, which is an indication of abuse. Snorting trazodone intensifies some of the drug’s sedating effects. Trazodone won’t produce a euphoric high that is similar with commonly abused drugs; however, it can have a sedative effect and can produce certain types of cognitive impairment.
What Are the Symptoms of Trazodone Overdose?
When an individual is addicted to trazodone, he/she will exhibit physical, mental, emotional, and psychological signs and symptoms. But, it could be difficult to identify that a person is addicted to trazodone because the person who is abusing trazodone will try to hide their addiction from people, especially their loved ones and the physician.
Below is a list of signs that an individual may be abusing trazodone:
- Unpredictable ability to keep doctor appointments.
- General decline in functioning.
- Asks for early refill of medication.
- Indifference to health concerns and side effects.
- Sudden demands for dosage increases from an otherwise stable patient on a lower dose of trazodone or other antidepressants.
Other signs of trazodone abuse include:
- Insomnia
- Talkativeness
- Erectile dysfunction
- Violent actions and thoughts
- Panic attacks
- Convulsions
- Aggression
- Mood swings
- Abdominal pains
- Nightmares
- Itchy eyes
- Blurred vision
- Excessive sweating
- Tremors
- Memory problems
The type and severity of these side effect symptoms vary from person to person.
Can You Experience Withdrawal from Trazodone?
Since trazodone works by acting on the brain chemistry, stopping the medication suddenly can cause some side effects. The withdrawal that a person will experience from suddenly stopping trazodone will be influenced by factors such as the dosage of trazodone that is taken, time span of trazodone use, how quickly the person tapers, and individual physiology. People who have been taking trazodone for several years are likely to experience more severe withdrawals than those who have only taken the drug for a couple of months. It has been noted that in many cases, the longer the time span of taking trazodone, the more difficult it is to withdraw from it.
Individuals who are taking a higher dose of trazodone will have more difficulty withdrawing from the drug. This is because their bodies have become dependent on that specific dose for them to function. If they discontinue from a higher dose, it will lead to longer withdrawal duration as well as more extreme symptoms.
The withdrawal symptoms related to trazodone and other antidepressants are real and must be done under medical supervision. Typically, a physician will taper down the medication dosage to safely transition the patient off the medication and minimize any side effects.
What Are the Symptoms of Trazodone Withdrawal?
Some of the withdrawal symptoms of trazodone are:
- Irritability
- Nervousness
- Aggression
- Blurred vision
- Loss of consciousness
- Muscle pain
- Headache
- Lack of concentration
- Impaired speech
- Loss of appetite
- Constipation
- Migraines
- Dizziness
- Depersonalization
- Disorientation
- Itching
- Anxiety
- Insomnia
People who are coming off of trazodone must be closely monitored to lessen the risk caused by possible clinical depression or other mental health problems.
For many people, the withdrawal symptoms of trazodone improve over time. However, for people who take trazodone to sleep, stopping the drug abruptly may cause the insomnia to come back and it could be worse than before.
Withdrawal is not the only consequence of stopping the intake or abuse of trazodone. Severe depression and suicidal thoughts could also develop.
What Are the Complications of Trazodone Overdose?
The complications of trazodone overdose are rooted at the extreme effects of trazodone in the body. These may include neurologic, cardiovascular, respiratory, and gastrointestinal complications. Trazodone overdose complications include:
- Drowsiness – Trazodone has antihistamine effects which can result in depression of the central nervous system. Drowsiness could be potentiated with increased ingestion of the drug and could lead to more alteration in the mental status of the person. Severe trazodone overdoses may result in coma.
- Vomiting – Vomiting is a possible trazodone overdose complication due to its affectation to the gastrointestinal tract.
- Breathing problems – When the central nervous system is depressed, it could lead to respiratory depression. People who may have trazodone overdose typically experience decreased respiratory rate and shortness of breath.
- Priapism – Priapism is the prolonged erection of the penis even in the absence of sexual stimulation. This disorder is due to the antagonistic effect of the medicine in the alpha-adrenergic receptors leading to vasodilatation. The lengthened vasodilatation in the penis leads to an in increased blood flow to the area resulting in constant erection. Priapism could be painful and is considered a medical emergency because it could lead to a possible ischemia to the tissues. It could also happen in the clitoris of women.
- Arrhythmia – Cardiac arrhythmias are a possible trazodone overdose complication. This is due to its affectation to the adrenergic rectors in the heart which leads to cardiac irregularities. The most common arrhythmia that an individual experiencing a trazodone overdose could experience is premature ventricular contractions.
- Seizures – A trazodone overdose can result in unstable electrical impulses of the neurons in the brain. Thus, leading to seizures.
- Decreased white blood cell counts – Trazodone could have the effects of decreasing the white blood cell count in the body which can lead to the development of infections.
An overdose of trazodone could be fatal when people have taken very large doses of this drug. Death could also occur due to the central nervous system and respiratory system depression as well as cardiac failure.